|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| The link between climate change and extreme weather |
|
| |
 What is extreme weather? What is extreme weather?
Extreme weather and climate events are events that: |
- typically don't happen very
frequently, such as droughts or floods that have
historically occurred on average only once in 100 years.
- vary from "the norm" in severity or
duration, like heat waves.
- have severe impacts, like
hurricanes.
|
|
Scientists study many aspects of change in extreme weather
and climate events. These include: |
- Frequency: Are events occurring more
often than they did in the past?
- Intensity: Are events getting more
severe, with the potential for more damaging effects?
- Duration: Are events lasting longer
than "the norm"?
- Timing: Are events occurring earlier
or later in the season or the year than they used to?
|
|
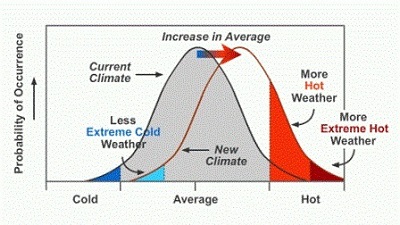
Extreme weather is typically rare. But climate change is
increasing the odds of more extreme weather events taking
place. |
 Extreme
Weather Extreme
Weather
Establishing the most likely causes behind an extreme
weather event can be challenging, since these events are due
to combinations of multiple factors, including natural
variability.
Nevertheless, scientists have been able to draw a connection
between some types of extreme climate patterns—an even some
individual events—and climate change. A good way to think
about this connection is to focus on whether an extreme
weather event was made more likely by climate change.
There have been changes in some types of extreme weather
events in the United States over the last several decades,
including more intense and frequent heat waves, less
frequent and intense cold waves, and regional changes in
floods, droughts, and wildfires. This rise in extreme
weather events fits a pattern you can expect with a warming
planet. Scientists project that climate change will make
some of these extreme weather events more likely to occur
and/or more likely to be severe. |
|
|
Trends in Specific Extreme Weather
Events - Heat Waves |
- Why does it matter? Heat waves can
have serious health consequences, particularly for older
adults, young children, the poor, and people with
certain pre-existing health conditions, like asthma or
heart disease. Excessive heat can also kill or injure
crops and livestock, and it can lead to power outages as
heavy demand for air conditioning strains the power
grid.
- How does it relate to climate
change? Even a small rise in average temperature brought
on by climate change can boost the odds of extreme heat
and heat waves.
- What's happening? Climate change has
increased the likelihood of more frequent and more
severe heat waves. Heat waves have generally become more
frequent and intense across the United States in recent
decades, particularly in the western United States
(including Alaska). The impacts of heat waves are
greatest in the Northeast and Midwest, and in urban
areas, where the urban heat island effect increases
vulnerability to heat-related health impacts.
- What's ahead? Heat waves are
expected to become more frequent, longer, and more
intense in the years ahead. The number of extremely hot
days is projected increase throughout the United States.
- How sure is the science? Scientists
are highly confident that heat waves and other extreme
heat events have and will continue to become more
frequent and intense due to climate change.
|
|
 Adaptation:
Reducing the Threat of Climate Change and Preparing for
Impacts Adaptation:
Reducing the Threat of Climate Change and Preparing for
Impacts
Extreme weather and climate events pose a serious threat to
the health and welfare of American families and businesses.
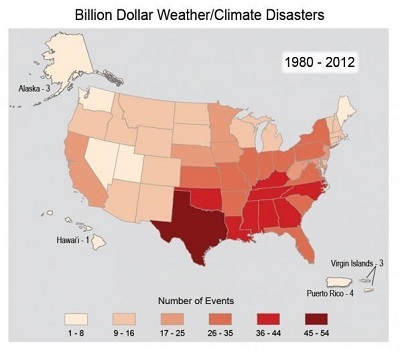
Picture - This map
summarizes the number of times each state has been affected
by weather and climate events over the past 30 years that
have resulted in more than a billion dollars in damages. The
Southeast has been affected by more billion-dollar disasters
than any other region. The primary disaster type for coastal
states such as Florida is hurricanes, while interior and
northern states in the region also experience sizeable
numbers of tornadoes and winter storms.
For instance, between 2011 and 2013, the United States
experienced 32 weather events that each caused at least one
billion dollars in damages. 2012 ranks as 2nd costliest year
on record, with more than $110 billion in damages.
EPA is taking a number of common-sense actions to reduce
greenhouse gas emissions and help cities and towns build
more resilient communities to prepare for the impacts of a
changing climate, including the weather extremes described
above. |
|
|
Key Points |
- Extreme weather events are becoming
more frequent and/or severe around the world. This is
consistent with what we expect with a warming planet.
- Increasingly frequent and/or severe
weather events have serious consequences for society and
ecosystems.
- Between 2011 and 2013, the United
States experienced 32 weather events that each caused at
least one billion dollars in damages.
- Changes in some weather events are
more closely linked to climate change than others.
- Understanding the links between
climate change and extreme events can help us plan for
the future.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Additional Climate Change Information |
Climate Change and Carbon Dioxide
(Beginner - Listening,
reading)
A video lesson to
help with your understanding of climate change
and carbon dioxide.
The English is
spoken at 75% of normal speed.
Great English listening and reading practice. |
Carbon Dioxide and Climate Change
(Beginner - Listening,
reading)
A video lesson to
help with your understanding of carbon dioxide
and climate change.
The English is
spoken at 75% of normal speed.
Great English listening and reading practice. |
Environmental Group Warns Earth's Health at Risk
(Beginner - Listening,
reading)
A video lesson to
help with your understanding of climate change.
The English is
spoken at 75% of normal speed.
Great English listening and reading practice.
A report by the World Wildlife Fund looked at thousands of animal populations
and found they have dropped significantly in 40 years. |
Sea Levels Rising at Fastest Rate in 3,000 years
(Beginner - Listening,
reading)
A video lesson to
help with your understanding of climate change.
The English is
spoken at 75% of normal speed.
Great English listening and reading practice.
A group of scientists say sea levels are rising at record rates. Another group
found that January temperatures in the Arctic reached a record high. |
Capturing CO2 Gas Is Not Easy
(Beginner - Listening,
reading)
A video lesson to
help with your understanding of climate change.
The English is
spoken at 75% of normal speed.
Great English listening and reading practice.
Most scientists agree that carbon-dioxide gas is partly to blame for climate
change: rising global temperatures. But capturing the CO2 gas released by power
stations is costly and difficult. |
Growth, Climate Change Threaten African Plants and
Animals
(Beginner - Listening,
reading)
A video lesson to
help with your understanding of climate change.
The English is
spoken at 75% of normal speed.
Great English listening and reading practice.
Researchers believe Africa may lose as much as 30 percent of its animal and
plant species by the end of this century. |
|
|
|
|
Search Fun Easy English |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
About
Contact
Copyright
Resources
Site Map |