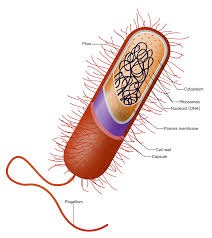
 |
| A typical prokaryote
cell. |
Cell Biology
Cell biology (also cellular biology or cytology) is a
branch of biology studying the structure and function of
the cell, also known as the basic unit of life. Cell
biology encompasses both prokaryotic and eukaryotic
cells and can be divided into many sub-topics which may
include the study of cell metabolism, cell
communication, cell cycle, biochemistry, and cell
composition. The study of cells is performed using
several techniques such as cell culture, various types
of microscopy, and cell fractionation. These have
allowed for and are currently being used for discoveries
and research pertaining to how cells function,
ultimately giving insight into understanding larger
organisms. Knowing the components of cells and how cells
work is fundamental to all biological sciences while
also being essential for research in biomedical fields
such as cancer, and other diseases. Research in cell
biology is interconnected to other fields such as
genetics, molecular genetics, biochemistry, molecular
biology, medical microbiology, immunology, and
cytochemistry. |
|