|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
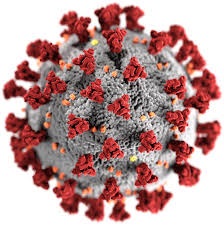 |
| SARS-CoV-2, a member
of the subfamily Coronavirinae. |
Virus
A virus is a microscopic parasite that can infect living
organisms and cause disease. It can make copies of
itself inside another organism's cells. Viruses consist
of nucleic acid and a protein coat. Usually the nucleic
acid is RNA; sometimes it is DNA. Viruses are able to
cause many types of diseases, such as polio, ebola and
hepatitis. Virology is the study of viruses.
Viruses reproduce by getting their nucleic acid strand
into a prokaryote or eukaryote (cell). The RNA or DNA
strand then takes over the cell machinery to reproduce
copies of itself and the protein coat. The cell then
bursts open, spreading the newly created viruses. All
viruses reproduce this way, and there are no free-living
viruses. Viruses are everywhere in the environment, and
all organisms can be infected by them.
Viruses are so much smaller than bacteria. They were not
visible until the invention of the electron microscope.
A virus has a simple structure, it has no internal
cellular structure, no cell wall or cell membrane, just
the protein coat that holds the string of nucleic acid.
Viruses live and reproduce in the cell which is why
medication such as antibiotics cannot help fight against
the virus as it cannot enter the cell without damaging
the cell.
With eukaryotic cells, the virus protein coat is able to
enter the target cells via certain cell membrane
receptors. With prokaryote bacteria cells, the
bacteriophage physically injects the nucleic acid strand
into the host cell.
Viruses have the following characteristics: |
- Infectious particles, causing many
types of disease;
- Contain nucleic acid core RNA or
DNA;
- Surrounded by a protective protein
coat;
|
When the host cell has finished making more viruses, it
undergoes lysis, or breaks apart. The viruses are released
and are then able to infect other cells. Viruses can remain
intact for a long time, and will infect cells when the time
and conditions are right.
Some special viruses are worth noting. Bacteriophages have
evolved to enter bacterial cells, which have a different
type of cell wall from eukaryote cell membranes. Envelope
viruses, when they reproduce, cover themselves with a
modified form of the host cell membrane, thus gaining an
outer lipid layer that helps entry. Some of our most
difficult to combat viruses, like influenza and HIV, use
this method.
Viral infections in animals trigger an immune response which
usually kills the infecting virus. Vaccines can also produce
immune responses. They give an artificially acquired
immunity to the specific viral infection. However, some
viruses (including those causing AIDS and viral hepatitis)
escape from these immune responses and cause chronic
infections. Antibiotics have no effect on viruses, but there
are some other drugs against viruses. |
|
Genome
There are a many genomic structures in viruses. As a
group they have more structural genomic diversity than
plants, animals, archaea, or bacteria. There are
millions of different types of viruses, but only about
5,000 of them have been described in detail.
A virus has either RNA or DNA genes and is called an RNA
virus or a DNA virus respectively. The vast majority of
viruses have RNA genomes. Plant viruses tend to have
single-stranded RNA genomes and bacteriophages tend to
have double-stranded DNA genomes.
Replication cycle
Viral populations do not grow through cell division,
because they do not have cells. Instead, they use the
machinery and metabolism of a host cell to produce many
copies of themselves, and they assemble (put together)
in the cell.
The life cycle of viruses differs greatly between
species but there are six basic stages in the life cycle
of viruses: |
- Attachment is a specific binding
between viral capsid proteins and specific receptors on
the host cellular surface.
- Penetration follows attachment:
Virions (single virus particles) enter the host cell
through receptor-mediated endocytosis or membrane
fusion. This is often called viral entry. The infection
of plant and fungal cells is different from that of
animal cells. Plants have a rigid cell wall made of
cellulose, and fungi one of chitin. This means most
viruses can only get inside these cells by force. An
example would be: a virus travels on an insect vector
which feeds on plant sap. The damage done to cell walls
would let the virus get in. Bacteria, like plants, have
strong cell walls that a virus must get through to
infect the cell. However, bacterial cell walls are much
thinner than plant cell walls, and some viruses have
mechanisms that inject their genome into the bacterial
cell across the cell wall, while the viral capsid
remains outside.
- Uncoating is a process in which the
viral capsid is removed: This may be by degradation by
viral enzymes or host enzymes or by simple dissociation;
the end-result is the releasing of the viral nucleic
acid.
- Replication of viruses involves
multiplication of the genome. This usually requires
production of viral messenger RNA (mRNA) from "early"
genes. This may be followed, for complex viruses with
larger genomes, by one or more further rounds of mRNA
synthesis: "late" gene expression is of structural or
virion proteins.
- Following the structure-mediated
self-assembly of the virus particles, some modification
of the proteins often occurs. In viruses such as HIV,
this modification (sometimes called maturation) occurs
after the virus has been released from the host cell.
- Viruses can be released from the
host cell by lysis, a process that kills the cell by
bursting its membrane and cell wall. This is a feature
of many bacterial and some animal viruses.
|
In some viruses the viral genome is put by genetic
recombination into a specific place in the host's
chromosome. The viral genome is then known as a "provirus"
or, in the case of bacteriophages a "prophage".
Whenever the host divides, the viral genome is also
replicated. The viral genome is mostly silent within the
host; however, at some point, the provirus or prophage may
give rise to active virus, which may lyse the host cells.>
Enveloped viruses (e.g. HIV) typically are released from the
host cell after the virus acquires its envelope. The
envelope is a modified piece of the host's plasma membrane.
Genetic material and replication
The genetic material within virus particles, and the method
by which the material is replicated, varies considerably
between different types of viruses.
RNA viruses - Replication usually takes place in the
cytoplasm. RNA viruses can be placed into four different
groups depending on their modes of replication. All RNA
viruses use their own RNA replicase enzymes to create copies
of their genomes.
DNA viruses - The genome replication of most DNA viruses
takes place in the cell's nucleus. Most DNA viruses are
entirely dependent on the host cell's DNA and RNA
synthesising machinery, and RNA processing machinery.
Viruses with larger genomes may encode much of this
machinery themselves. In eukaryotes the viral genome must
cross the cell's nuclear membrane to access this machinery,
while in bacteria it need only enter the cell.
Reverse transcribing viruses - Reverse transcribing viruses
with RNA genomes (retroviruses) use a DNA intermediate to
replicate. Those with DNA genomes (pararetroviruses) use an
RNA intermediate during genome replication. They are
susceptible to antiviral drugs that inhibit the reverse
transcriptase enzyme. An example of the first type is HIV,
which is a retrovirus. Examples of the second type are the
Hepadnaviridae, which includes Hepatitis B virus. |
|
Host defense mechanisms
Innate immune system
The body's first line of defence against viruses is the
innate immune system. This has cells and other
mechanisms which defend the host from any infection. The
cells of the innate system recognise, and respond to,
pathogens in a general way.
RNA interference is an important innate defence against
viruses. Many viruses have a replication strategy that
involves double-stranded RNA (dsRNA). When such a virus
infects a cell, it releases its RNA molecule. A protein
complex called dicer sticks to it and chops the RNA into
pieces. Then a biochemical pathway, called the RISC
complex, starts up. This attacks the viral mRNA, and the
cell survives the infection.
Rotaviruses avoid this by not uncoating fully inside the
cell and by releasing newly produced mRNA through pores
in the particle's inner capsid. The genomic dsRNA
remains protected inside the core of the virion.
The production of interferon is an important host
defence mechanism. This is a hormone produced by the
body when viruses are present. Its role in immunity is
complex; it eventually stops the viruses from
reproducing by killing the infected cell and its close
neighbours.
Adaptive immune system
Vertebrates have a second, more specific, immune system.
It is called the adaptive immune system. When it meets a
virus, it produces specific antibodies that bind to the
virus and render it non-infectious. Two types of
antibodies are important.
The first, called IgM, is highly effective at
neutralizing viruses but is produced by the cells of the
immune system only for a few weeks. The second, called
IgG, is produced indefinitely. The presence of IgM in
the blood of the host is used to test for acute
infection, whereas IgG indicates an infection sometime
in the past. IgG antibody is measured when tests for
immunity are carried out.
Another vertebrate defence against viruses is
cell-mediated immunity. It involves immune cells known
as T cells. The body's cells constantly display short
fragments of their proteins on the cell's surface, and,
if a T cell recognises a suspicious viral fragment
there, the host cell is destroyed by killer T cells and
the virus-specific T-cells proliferate. Cells such as
macrophages are specialists at this antigen
presentation.
Evading the immune system
Not all virus infections produce a protective immune
response. These persistent viruses evade immune control
by sequestration (hiding away); blocking antigen
presentation; cytokine resistance; evading natural
killer cell activity; escape from apoptosis (cell
death), and antigenic shift (changing surface proteins).
HIV evades the immune system by constantly changing the
amino acid sequence of the proteins on the surface of
the virion. Other viruses, called neurotropic viruses,
move along nerves to places the immune system cannot
reach.
Evolution
Viruses do not belong to any of the six kingdoms. They
do not meet all the requirements for being classified as
a living organism because they are not active until the
point of infection. However, that is just a verbal
point.
Obviously, their structure and mode of operation means
they have evolved from other living things, and the loss
of normal structure occurs in many endoparasites. The
origins of viruses in the evolutionary history of life
are unclear: some may have evolved from plasmids –
pieces of DNA that can move between cells – while others
may have evolved from bacteria. In evolution, viruses
are an important means of horizontal gene transfer,
which increases genetic diversity.
Recent discoveries
A recent project discovered nearly 1500 new RNA viruses
by sampling over 200 invertebrate species. "The research
team... extracted their RNA and, using next-generation
sequencing, deciphered the sequence of a staggering 6
trillion letters present in the invertebrate RNA
libraries". The research showed that viruses changed
bits and pieces of their RNA by a variety of genetic
mechanisms. "The invertebrate virome [shows] remarkable
genomic flexibility that includes frequent
recombination, lateral gene transfer among viruses and
hosts, gene gain and loss, and complex genomic
rearrangements".
Largest virus
A group of large viruses infect amoebae. The largest is
Pithovirus. Others in order of size are Pandoravirus,
then Megavirus, then Mimivirus. They are bigger than
some bacteria, and visible under a light microscope. |
|
Uses
Viruses are used widely in cell biology. Geneticists
often use viruses as vectors to introduce genes into
cells that they are studying. This is useful for making
the cell produce a foreign substance, or to study the
effect of introducing a new gene into the genome.
Eastern European scientists have used phage therapy as
an alternative to antibiotics for some time, and
interest in this approach is increasing, because of the
high level of antibiotic resistance now found in some
pathogenic bacteria. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Search Fun Easy English |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
About
Contact
Copyright
Resources
Site Map |