|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
 |
| Solutions of
substances in reagent bottles, including
ammonium hydroxide and nitric acid, illuminated
in different colors. |
Chemistry
Chemistry is a branch of science that deals with
chemical elements and compounds, and how these things
work together. It is the study of the materials (things)
that make up our bodies and everything in the world
around us.
History
Before 1600, people studied substances to figure out how
to do things such as turn lead into gold, but no one
managed to do that. This was called alchemy. Alchemists
(people that did alchemy) did discover some useful
things, though. Sulphuric acid and nitric acid were two
substances that they discovered. Only a few elements
were known. Some of them are mercury, silver, gold, and
carbon.
Chemistry began as a true science during the 1600s. This
is when chemists discovered the simplest substances that
make up all other substances. These simple substances
are called elements. One of the things that they learned
is that gold and lead are two different elements, so you
can not change one into the other by a chemical
reaction. The first element discovered after 1600 was
phosphorus, a strange white glowing solid.
Elements were discovered more and more rapidly. People
separated the air into many parts and isolated the noble
gases from it. They also processed special minerals from
a mine in Sweden to get rare earth metals. Radioactivity
was also discovered. Today chemists have discovered 118
different elements. Some are very common, like oxygen.
Many are very rare and expensive, like platinum. Some
cannot be found on earth and can only be made in labs,
like rutherfordium.
Since the 1920s, the increased understanding of physics
has changed chemists' theories about chemical reactions.
With smaller and faster computers, chemists have built
better tools for analyzing substances. These tools have
been sent to study chemicals on Mars. Police also use
those tools to study evidence from crime scenes. |
|
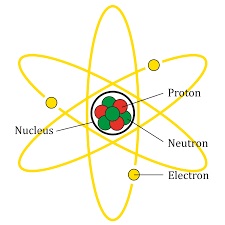 |
| A diagram of an atom
based on the Bohr model. |
Types of chemistry
There are several types of chemistry. Analytical
chemistry looks at which chemicals are in things. For
example, looking at how much arsenic is in food. Organic
chemistry looks at things that have carbon in them. For
example, making acetylene. Inorganic chemistry looks at
things that do not have carbon in them. One example is
making an integrated circuit.
A large area of chemistry is polymer chemistry. This
looks at plastics. One example is making nylon. Because
plastics are made of carbon, polymer chemistry is part
of organic chemistry. Another area is biochemistry. This
looks at the chemistry of living things. An example
would be seeing how arsenic poisons people. Biochemistry
is also part of organic chemistry. There are many other
small branches of chemistry. |
|
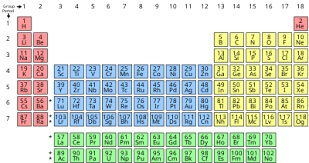 |
| Standard form of the
periodic table of chemical elements. The colors
represent different categories of elements. |
Concepts of chemistry
Basic concepts
The basic unit of an element is called an atom. An atom
is the smallest building block that you can cut an
element into without the element breaking down (turning
into a lighter element, for example through nuclear
fission or radioactive decay). A chemical compound is a
substance made up of two or more elements. In a
compound, two or more atoms are joined together to form
a molecule. The tiniest speck of dust or drop of liquid,
that one can see is made up of many millions or billions
of these molecules. Mixtures are substances where
chemicals are mixed but not reacted. An example would be
mixing sand and salt. This can be undone again to
produce salt and sand separately. Chemical compounds are
changed by a chemical reaction. An example would be
heating sodium bicarbonate, common baking soda. It will
make water, carbon dioxide, and sodium carbonate. This
reaction cannot be undone.
Mole
A mole is a very large amount of atoms
(602,214,150,000,000,000,000,000 atoms). The atomic mass
of an element can be used to see how much of the element
makes a mole. For example, the atomic mass of copper is
about 63.55. That means about 63.55 grams of copper
metal has a mole of atoms. The atomic mass of chlorine
is about 35.45. That means 35.45 grams of chlorine has a
mole of atoms in it.
Moles can be used to see how many molecules are in
chemical compounds, too. Copper(II) chloride is an
example. CuCl2 is its chemical formula. There is one
copper atom (63.55) and two chlorine atoms (35.45 · 2 =
70.90). Add all the molar masses of the elements
together to get the molar mass of the chemical compound
(63.55 + 70.90 = 134.45). That means in 134.45 grams of
copper(II) chloride, there is one mole of copper(II)
chloride molecules. This concept is used to calculate
how much chemicals are needed in a chemical reaction if
no reactants (chemicals that are reacted) should be
left. If too much reactant is used, there will be some
reactants left in the chemical reaction.
Acids and bases
Acids and bases are common chemicals. Acids release H+
ions when in water, and bases release OH− ions when in
water. Acids can react with bases. The H+ ion is taken
from the acid by the base. This makes water, H2O. A salt
is also made when an acid and a base react together. An
example would be reacting hydrochloric acid (HCl) and
sodium hydroxide (NaOH). Hydrochloric acid releases H+
and Cl- ions in water. The base releases Na+ and OH-
ions. The H+ and the OH- react to make water. There is a
solution of sodium chloride (NaCl) left. Sodium chloride
is a salt. |
|
 |
| An oil painting of a
chemist (by Henrika Šantel in 1932). |
Usefulness
Chemistry is very useful in everyday life and makes up
the foundation of many branches of science. Most objects
are made by chemists (people who do chemistry). Chemists
are constantly working to find new and useful
substances. Chemists make new drugs and materials like
paints that we use every day.
Safety
Many chemicals are harmless, but there are some
chemicals that are dangerous. For example, mercury(II)
chloride is very toxic. Chromates can cause cancer.
Tin(II) chloride pollutes water easily. Hydrochloric
acid can cause bad burns. Some chemicals like hydrogen
can explode or catch fire. To stay safe, chemists
experiment with chemicals in a chemical lab. They use
special equipment and clothing to do reactions and keep
the chemicals contained. The chemicals used in drugs and
in things like bleach have been tested to make sure they
are safe if used correctly. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Search Fun Easy English |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
About
Contact
Copyright
Resources
Site Map |