|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
 |
| Map showing location
of Africa. |
Africa
Africa is the second largest continent in the world
(after Asia). It makes up about a fifth of the world's
land. It is surrounded by large areas of water. There
are 54 fully recognised and independent countries in
Africa, and 14.7% (1.216 billion) of the world's
population lives there. It is thought to be the
continent where the first humans evolved.
History
The history of Africa begins from the first modern human
beings and leads to its present difficult state as a
politically developing continent.
Africa's ancient historic period includes the rise of
Egyptian civilization, the further development of
societies outside the Nile River Valley and the
interaction between them and civilizations outside of
Africa. In the late 7th century North and East Africa
were heavily influenced by the spread of Islam. That led
to the appearance of new cultures such as those of the
Swahili people, and the Mali Empire, whose king, Musa
Keita I, became one of the richest and most influential
people of the early 14th century. This also led to an
increase in the slave trade that had a very bad
influence for the development of the whole continent
until the 19th century. |
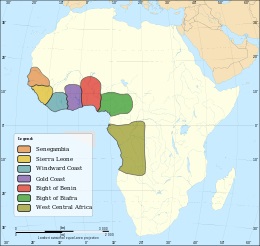 |
| Major slave trading
regions of Africa, 15th–19th centuries. |
Slavery
Slavery has long been practised in Africa. Between the
seventh and twentieth centuries, the Arab slave trade
took 18 million slaves from Africa via trans-Saharan and
Indian Ocean routes.
Between the fifteenth and the nineteenth centuries (500
years), the Atlantic slave trade took an estimated 7–12
million slaves to the New World.
Between 1808 and 1860, the British Navy captured
approximately 1,600 slave ships and freed 150,000
Africans who were aboard.
Colonialism
In the late nineteenth century, the European powers
occupied much of the continent, creating many colonial
and dependent territories. They left only three fully
independent states: Darwiish State, (also spelled
Daraawiish State), Ethiopia (known to Europeans as
"Abyssinia"), and Liberia.
Egypt and Sudan were never formally incorporated into
any European colonial empire. However, after the British
occupation of 1882, Egypt was effectively under British
administration until 1922. |
 |
| The Great Pyramids
of Giza are regarded as one of the greatest
architectural feats of all times and are one of
Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. |
Modern history
African independence movements had their first success
in 1951 when Libya became the first former colony to
become independent. Modern African history has been full
of revolutions and wars as well as the growth of modern
African economies and democratization across the
continent.
A civil war in the Democratic Republic of the Congo
(formerly Zaire) began in 1998. Neighbouring African
countries have become involved. Since the conflict
began, 5,5 million are estimated to have died because of
it.
Political associations such as the African Union offer
hope for greater co-operation and peace between the
continent's many countries. |
|
Climate
From north to south, Africa has most types of climate.
In sequence from the north: |
- Alpine and mediterranean climate
- Dry sandy desert
- Fairly dry savannah (grassland)
- Rain forest
- More grassland
- More deserts
- Table Mountain
|
Running north-east to the south is the East African Great
Rift Valley. This has mountains, volcanoes, deep rifts and
valleys, rivers and lakes.
In fact Africa has examples of most of the Earth's climate
types.
Rainfall
Much of North Africa is dry and hot: it is dominated by the
Sahara Desert and does not receive much rain. In Saharan
Africa there are few rivers or other water sources.
Underground water sources, such as springs are very
important in the desert. These often form oases. An oasis is
an area of vegetation (plant life) surrounded by desert.
In that part of the world the wind comes mostly from the
east. That does bring rain, but the Himalayas and the
Tibetan Plateau blocks the monsoon rain and prevents it
getting to North Africa. Also, the Atlas Mountains near the
north coast of Africa prevent rain from coming in from the
north. That is another rain shadow.
These two rain shadows are mainly responsible for the Sahara
desert.
Conditions and winds are different further south, where huge
amounts of rain falls near the equator. The equator runs
across the middle of Africa (see red line drawn on map).
That means much of Africa is between the two tropics: |
- Tropic of Cancer
- Tropic of Capricorn
|
Plants and animals
Africa has a lot of wildlife. There are many types of
animals there. In particular, it is now the only continent
that has many native species of large mammals. Some of them
occur in very large numbers. There are antelope, buffalo,
zebra, cheetah, elephant, lion, giraffe, rhinoceros, apes,
hyaena, and a lot more. Over 2,000 types of fish live in
African lakes and rivers. |
 |
| A musician from
South Africa. |
Politics
The African Union (AU) is an international organisation. It
aims to transform the African Economic Community, a
federated commonwealth, into a state under established
international conventions. The African Union has a
parliamentary government, known as the African Union
Government, consisting of legislative, judicial and
executive organs. It is led by the African Union President
and Head of State, who is also the President of the Pan
African Parliament. A person becomes President of the AU by
being elected to the PAP, and then gaining majority support
in the PAP.
Extensive human rights abuses still occur in several parts
of Africa, often under the oversight of the state. Most of
such violations occur for political reasons, often as a side
effect of civil war. Countries where major human rights
violations have been reported in recent times include
Uganda, Sierra Leone, Liberia, Sudan, Zimbabwe, and Côte
d'Ivoire.
People
People who come from Africa are called Africans. People
north of the Sahara are called Maghrebis and people on the
south are called Subsaharans. Languages in eastern Africa
include Swahili, Oromo and Amharic. Languages in western
Africa include Lingala, Igbo and Fulani. The most populated
country in Africa is Nigeria. |
|
African diaspora
Countries with significant African descendents outside
Africa: |
- Haiti: 98%
- Saint Kitts and Nevis: 96.9%
- Anguilla: 91.4%
- Bahamas: 86.1%
- Barbados: 81.1%
- Jamaica: 76.3%
- Dominican Republic: 71.1%
- Cayman Islands: 60.0%
- Trinidad and Tobago: 39.5%
- Cuba: 34.9%
- Turks and Caicos: 34.0%
- Belize: 29.8%
- Venezuela: 24.0%
- Panama: 22.0%
- Colombia: 21.0%
- Brazil: 13-19%
- United States: 12.9%
- Puerto Rico: 6.9%
- Argentina: less than 2%
|
|
|
Key facts about Africa |
- Africa is the second-largest
continent (after Asia) in the world with 54
countries.
- Africa is surrounded by large
areas of water.
- Africa's climate varies from
desert to rain forest. The desert is in the northern
part of Africa and the rainforest is in the middle
near the equator. The rest of Africa is mountains or
grasslands.
- Africa has many different kinds
of wildlife, each living in a climate that is best
for them.
- Africa has been influenced by
Egyptian civilization and by Islam.
- Slavery has been practiced in
Africa for centuries. The Arab slave trade took 18
million slaves from Africa and the Atlantic slave
trade took 7-12 million slaves to the New World.
- In the late 19th century,
different European powers occupied many of the
countries in Africa.
- In 1951, Libya became the first
former colony to become independent.
- The African Union was made to
help keep the peace between Africa's many countries.
|
 Kiddle: Africa Kiddle: Africa
Wikipedia: Africa |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Search Fun Easy English |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
About
Contact
Copyright
Resources
Site Map |