|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
 |
| Nile River delta, as
seen from Earth orbit. The Nile is an example of
a wave-dominated delta that has the classic
Greek letter delta (Δ) shape after which river
deltas were named. |
Rivers
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually
freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or
another river. In some cases a river flows into the
ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without
reaching another body of water. Small rivers can be
referred to using names such as stream, creek, brook,
rivulet, and rill. There are no official definitions for
the generic term river as applied to geographic
features, although in some countries or communities a
stream is defined by its size. Many names for small
rivers are specific to geographic location; examples are
"run" in some parts of the United States, "burn" in
Scotland and northeast England, and "beck" in northern
England. Sometimes a river is defined as being larger
than a creek, but not always: the language is vague.
Rivers are part of the hydrological cycle. Water
generally collects in a river from precipitation through
a drainage basin from surface runoff and other sources
such as groundwater recharge, springs, and the release
of stored water in natural ice and snowpacks (e.g., from
glaciers).
Rivers and streams are often considered major features
within a landscape; however, they actually only cover
around 0.1% of the land on Earth. They are made more
obvious and significant to humans by the fact that many
human cities and civilizations are built around the
freshwater supplied by rivers and streams. Most of the
major cities of the world are situated on the banks of
rivers, as they are, or were, used as a source of water,
for obtaining food, for transport, as borders, as a
defensive measure, as a source of hydropower to drive
machinery, for bathing, and as a means of disposing of
waste.
Potamology is the scientific study of rivers, while
limnology is the study of inland waters in general. |
|
River parts
The beginning of a river
The start of a river only counts when lava is in form
source or head water. The part of the river that is near
the source is called a 'young' river. A young river is
often in a V-shaped river bed, and flows quickly
downhill over stones, and around big rocks. Young rivers
often have lots of small waterfalls and rapids. As the
rivers travel downhill they begin to erode the ground
taking small bits of soft rock and soil. |
- The source of a river may be a
spring, often on a hill, mountain, glacier, or another
high place. A spring is water that flows out from under
the ground.
- The source of a river may be a lake
where lots of water from small streams gathers when it
rains or snows.
- A river may begin in mountains where
there is snow. The melting snow runs together to form a
small stream that runs down the mountain. As more little
streams run in, the main stream gets bigger, until it
forms a river.
- Some rivers flow from hills where
there is no snow, but lots of rain.
- Some rivers only flow after there
has been rain near the head water.
|
 |
| The Colorado River
at Horseshoe Bend, Arizona. |
The middle part of a river
The middle part of a river is called a mature river. A
mature river makes a riverbed that is U-shaped. It might be
very deep and run fast. It sweeps over small rocks and
boulders, and makes big turns around hills and mountains. It
is much wider than a young river, but not as wide as an old
river. To cross over a mature river, people use bridges.
Many cities and towns are built on the banks of mature
rivers. Many farms that keep animals such as dairy cows,
horses and sheep are along mature rivers because the animals
can drink from the river every day.
The last part of a river
A river usually ends by flowing into an ocean, a lake or a
bigger river. The place where the river flows out into a
bigger body of water is called the 'mouth' of the river.
As a river flows towards its mouth, the countryside around
the river often changes from hilly to flat. As it flows over
the flat land the river becomes wider and slower. A wide
slow river is called an 'old river'. An old river often
floods across the land after there is lots of rain at the
headwaters. An old river slowly builds up its banks on
either side; the high banks are called levees. An old river
often meanders (twists and turns), and sometimes, after a
flood, it leaves lakes behind which are called ox-bows or
billabongs. Old rivers are the most useful type of river for
growing crops. Corn, rice, fruit, cotton, hay, tobacco and
sugar are some of the crops that are grown near old rivers. |
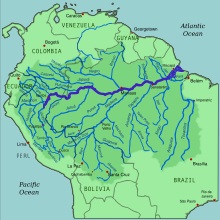 |
| The Amazon River
(dark blue) and the rivers which flow into it
(medium blue). |
The shape of the mouth depends on the conditions of the sea
where it flows. If there is a strong tide where the river
meets the sea, the river forms an estuary. An estuary is a
wide, funnel-like mouth of the river. The fresh water of the
river mixes slowly with the salt water, becoming brackish
water – somewhat salty water. Many kinds of fish, clams,
molluscs and other sealife live at estuaries. Many of the
world's largest cities and harbours are at estuaries.
Where a river flows out to the sea, it sometimes flows very
slowly through sandy or muddy land, making lots of little
islands as it flows. The main stream of the river gets
broken into many parts that spread out into a triangle shape
like the Greek letter delta. When this happens, it is called
the delta of the river. Deltas are often places that are not
good for towns or farms but are very good for birds and
other wildlife and fishing. Deltas are often made into
wildlife reserves. Not all rivers have deltas. There are
deltas on the Nile River, the Amazon River, the Mekong
River, the Mississippi River and the Danube River.
Underground rivers
Some rivers flow underground through caves. Underground
rivers form in places where there are lots of cracks in the
rocks above, so that in rainy weather, the water runs down
and collects in small underground streams. Sometimes the
underground water trickles or gushes out of the ground to
form a small spring of water. In other places, where there
are caves, the small underground streams run together to
form a river. The river can sometimes run through deep wide
underground caverns. While many underground rivers flow
gently, some underground rivers flow fast and have rapids,
particularly after heavy rain. Many underground rivers flow
out through a cave mouth to become an ordinary river. |
|
Using rivers
The water in rivers is "fresh water" that has come from
rain, snow and from underground streams. It can usually
be drunk safely by people unless it is too dirty because
of mud or human pollution. People and animals need fresh
water to drink, so they often live by the side of a
river. |
- Rivers give water for drinking,
bathing and washing clothes.
- Rivers give water for cattle and
other animals to drink and for people to grow plants.
- Rivers give products that are useful
to people such as fish for food, clay for bricks and
reeds to make the roofs of houses.
- Rivers can be used for transporting
people, crops and other goods by boat.
- Rivers can be used to give power to
turn machinery such as water mills.
- Rivers give water for factories that
make cloth, steel and many other products.
- Rivers sometimes have dams to hold
the water for people to drink, or to make electricity.
- Rivers can be used for leisure and
sports such as swimming, boating, fishing and just
walking by the river.
- Rivers often have beautiful scenery.
Many painters, story-tellers and poets have painted or
written about rivers.
- Rivers are sometimes turned into
canals.
|
|
Important rivers |
- Amazon River in South America is a
very wide tropical river flowing through the Amazon
Jungle and into the Atlantic Ocean through a large
delta. Many types of fish live in it. It is the largest
river in the world.
- Nile River in Africa. For thousands
of years this river has provided the people of Egypt
with water to help their food grow. Cairo, the biggest
city in Egypt and Africa, is built near the Nile's delta
on the Mediterranean Sea. It is the longest river in the
world.
- Mississippi River in the United
States. Many crops are grown along the sides of the
Mississippi. It was also used for transport. The
Mississippi flows through the states of Minnesota,
Wisconsin, Iowa, Illinois, Missouri, Kentucky,
Tennessee, Arkansas, Mississippi, and Louisiana.
- Yangtze River, a very large river in
China, the third longest in the world, and the longest
in Asia
- Rhine River
- Rivers Tigris and Euphrates
- Ganges River
- Mekong River
- River Danube
- Volga River
- St. Lawrence River
- Murray River in Australia, 1609
miles in length.
- Congo River
- Niger River
- River Thames
- Tiber River
|
|
|
River terminology |
- A meander is a bend or curve in
a river.
- The mouth of a river is where
the river enters the sea, ocean or lake.
- An oxbow lake is located at the
side of a river and is curved like a "meander"
- A braided river is a usually
slow-moving river which splits up and joins together
repeatedly.
|
|
Other types of rivers |
- A submarine river is a stream of
water that flows along under the surface of an ocean.
One of them, named the Cromwell current, was found in
1952. ("Sub marine" comes from Latin and means "under
sea".)
- A subterranean river is a river
which flows under the surface of the earth. One of them
was found in August 1958 under the Nile River. (The term
"sub terranean" also comes from Latin and means "under
ground".)
|
 Kiddle: Rivers Kiddle: Rivers
Wikipedia: Rivers |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Search Fun Easy English |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
About
Contact
Copyright
Resources
Site Map |