|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
Energy Balance
The earth-atmosphere energy balance is the balance
between incoming energy from the Sun and outgoing energy
from the Earth. Energy released from the Sun is emitted
as shortwave light and ultraviolet energy. When it
reaches the Earth, some is reflected back to space by
clouds, some is absorbed by the atmosphere, and some is
absorbed at the Earth's surface.
However, since the Earth is much cooler than the Sun,
its radiating energy is much weaker (long wavelength)
infrared energy. We can indirectly see this energy
radiate into the atmosphere as heat, rising from a hot
road, creating shimmers on hot sunny days.
The earth-atmosphere energy balance is achieved as the
energy received from the Sun balances the energy lost by
the Earth back into space. In this way, the Earth
maintains a stable average temperature and therefore a
stable climate. Using 100 units of energy from the sun
as a baseline the energy balance is as follows: |
|
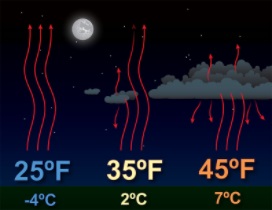 |
| How cloud cover can
affect nighttime temperatures. |
The absorption of infrared radiation trying
to escape from the Earth back to space is particularly
important to the global energy balance. Energy
absorption by the atmosphere stores more energy near its
surface than it would if there was no atmosphere.
The average surface temperature of the moon, which has
no atmosphere, is 0°F (-18°C). By contrast, the average
surface temperature of the Earth is 59°F (15°C). This
heating effect is called the greenhouse effect. |
|
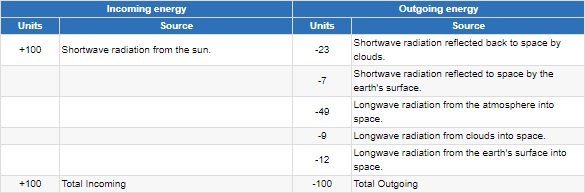 |
| At the top of the
atmosphere - Incoming energy from the sun
balanced with outgoing energy from the earth. |
|
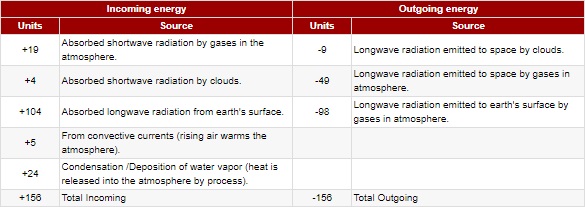 |
| The atmosphere
itself - Energy into the atmosphere is balanced
with outgoing energy from atmosphere. |
|
|
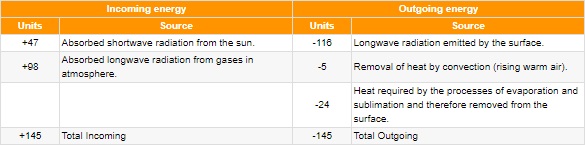 |
| At the earth's
surface - Energy absorbed is balanced with the
energy released. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Search Fun Easy English |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
About
Contact
Copyright
Resources
Site Map |