|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
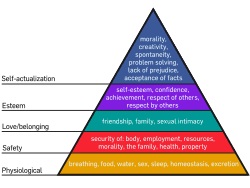 |
| Psychologist Abraham
Maslow in 1943 posited that humans have a
hierarchy of needs, and it makes sense to
fulfill the basic needs first (food, water etc.)
before higher-order needs can be met. |
Psychology
Psychology is the study of the mind and of thought,
feeling, and behaviour. It is an academic and applied
discipline which involves the scientific study of mental
functions and behaviours.
Psychology deals mainly with humans but also sometimes
with animals. Because psychology is difficult to study
as a whole, psychologists often only look at small parts
of it at one time. Psychology has much in common with
many other fields, and overlaps with many of them. Some
of these fields are medicine, ethology, computer
science, and linguistics.
In this field, a professional practitioner or researcher
is called a psychologist and is a social, behavioural,
or cognitive scientist. Psychologists attempt to
understand the role of mental functions in individual
and social behavior. They also explore the physiological
and neurobiological processes which underlie cognitive
functions and behaviours. |
|
Branches
Psychology has been split up into smaller parts called
branches. These are subjects in psychology that try to
answer a particular group of questions about how people
think. Some branches of psychology that are often
studied are: |
- Abnormal psychology tries to work
out what differences there are between people who are
healthy and people who have a mental illness.
- Clinical psychology is about finding
the best way to help people to recover from mental
illness.
- Cognitive psychology looks at how
people think, use language, remember and forget, and
solve problems.
- Cross-cultural psychology looks at
different ways of living and views of the world.
- Developmental psychology is
interested in how people develop and change through
their lives. This includes what used to be called "child
psychology".
- Educational or school psychology
tests and helps students to learn and make friends.
- Evolutionary psychology studies how
evolution may have shaped the way people think and do
things.
- Neuropsychology looks at the brain
and how it works to make people the way they are.
- Motivation: the root causes of
action
- Perceptual psychology asks questions
about how people make sense of what they see and hear
and how they use that information to get around.
- Social psychology looks into how
groups of people work together and how societies build
and work.
|
|
Methods
Scientific approaches
Psychology is a type of science, and research
psychologists use many of the same types of methods that
researchers from other natural and social sciences use.
Psychologists make theories to try to explain a behavior
or pattern they see. Based on their theory they make
some predictions. They then carry out an experiment or
collect other types of information that will tell them
whether their predictions were right or wrong.
Some types of experiments cannot be done on people
because the process would be too long, expensive,
dangerous, unfair, or otherwise unethical. There are
also other ways psychologists study the mind and
behavior scientifically, and test their theories.
Psychologists might wait for some events to happen on
their own; they might look at patterns among existing
groups of people in natural environments; or they might
do experiments on animals (which can be simpler and more
ethical to study).
Psychology shares other things with natural sciences, as
well. For example, a good psychological theory may be
possible to prove wrong. Just like in any natural
science, a group of psychologists can never be
completely sure that their theory is the right one. If a
theory can be proved wrong, but experiments do not prove
it wrong, then it is more likely that the theory is
accurate. This is called falsifiability.
Psychologists use many tools as part of their daily
work. Psychologists use surveys to ask people how they
feel and what they think. They may use special devices
to look at the brain and to see what it is doing.
Psychologists use computers to collect data as they
measure how people behave in response to pictures,
words, symbols, or other stimuli. Psychologists also use
statistics to help them analyze the data that they get
from their experiments.
Symbolic and subjective
approaches
Not all psychology is scientific psychology.
Psychodynamic psychology and depth psychology do things
like interpreting people's dreams to understand the
unconscious mind, as in older approaches to psychology
begun by Carl Jung who was particularly interested in
finding methods for measuring what kind of personality
people have.
Humanistic psychology and existential psychology also
believe that it is more important to understand personal
meaning than to find causes and effects of mental
processes and behaviours. |
|
Psychologists
Psychologists are people who work in the field of
psychology. A psychologist may work in either basic
research or applied research. Basic research is the
study of people or animals to learn more about them.
Applied research is using what was learned from basic
research to solve real-world problems. If he or she is
qualified as a clinical psychologist they may be a
therapist or counselor as well as a researcher.
To become a psychologist, a person must first get a
basic degree at a university and then go to graduate
school. A Master's degree, either MSc (Master of
Science) or MA (Master of Arts) allows beginning work,
like a school psychologist. A doctorate degree takes a
longer time because it includes doing research and
writing a detailed report called a dissertation or
thesis. The doctoral graduate uses the initials PhD or
DPhil (Doctor of Philosophy) after his or her name. Some
clinical psychologists earn a Doctor of Psychology
degree and use the initials PsyD after their name. The
American Psychological Association says that people need
a PhD (or PsyD and a current state license in the U.S.)
in order to call themselves a 'psychologist'.
The words psychologist and psychiatrist may be confused
with each other. A psychiatrist has graduated from
medical school and uses the initials MD or its
equivalent (MB ChB in London University, for example). A
psychiatrist or doctor may work with a psychologist:
they may prescribe and check on the effect of
medications. |
|
|
 Kiddle: Psychology Kiddle: Psychology
Wikipedia: Psychology |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Search Fun Easy English |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
About
Contact
Copyright
Resources
Site Map |