|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
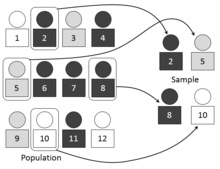 |
| Sampling is supposed
to collect of a representative sample of a
population. |
Bias
Bias means that a person prefers an idea and possibly
does not give equal chance to a different idea. Bias can
be influenced by a number of factors, such as popularity
(for example, a newspaper might be biased towards a
particular political party due to their employees
sharing the same political beliefs as that party).
Bias in an article or editorial would show one point of
view, using selected facts and quotes to support that
point of view. Facts or opinions that do not support the
point of view in a biased article would be excluded. For
example, an article biased toward riding a motorcycle
would show facts about the good gas mileage, fun, and
agility. An article biased against motorcycle riding
would show facts about risk of injury and noise, and
ignore positive facts about motorcycles. |
|
|
Bias in writing can also be shown by using bad or slang
words to refer to groups of people or things. "Broads"
rather than "women"; "murdercycles" rather than
"motorcycles". Words or phrasing that make wide
assumptions about races or groups of people also
indicates bias. "All Chinese people are good at math". |
|
|
Bias also means mistakes in measurements. For example, a
person may measure the height of another person wearing
shoes. The shoes make the height more than the same
person without shoes. If the extra height of the shoes
(extra bias) was not explained, someone might think that
the person had been measured without shoes on. Data with
extra parts not explained is called biased data. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Search Fun Easy English |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
About
Contact
Copyright
Resources
Site Map |