 |
| "5 − 2 = 3"
(verbally, "five minus two equals three"). |
Subtraction
Subtraction is an arithmetic operation that represents
the operation of removing objects from a collection.
Subtraction is signified by the minus sign, −. For
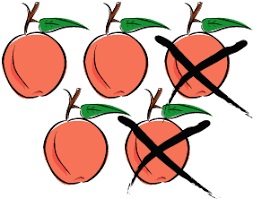
example, in the adjacent picture, there are 5 − 2
apples—meaning 5 apples with 2 taken away, resulting in
a total of 3 apples. Therefore, the difference of 5 and
2 is 3, that is, 5 − 2 = 3. While primarily associated
with natural numbers in arithmetic, subtraction can also
represent removing or decreasing physical and abstract
quantities using different kinds of objects including
negative numbers, fractions, irrational numbers,
vectors, decimals, functions, and matrices.
Subtraction follows several important patterns. It is
anticommutative, meaning that changing the order changes
the sign of the answer. It is also not associative,
meaning that when one subtracts more than two numbers,
the order in which subtraction is performed matters.
Because 0 is the additive identity, subtraction of it
does not change a number. Subtraction also obeys
predictable rules concerning related operations, such as
addition and multiplication. All of these rules can be
proven, starting with the subtraction of integers and
generalizing up through the real numbers and beyond.
General binary operations that follow these patterns are
studied in abstract algebra. |
|
Performing subtraction on natural numbers is one of the
simplest numerical tasks. Subtraction of very small
numbers is accessible to young children. In primary
education for instance, students are taught to subtract
numbers in the decimal system, starting with single
digits and progressively tackling more difficult
problems.
In advanced algebra and in computer algebra, an
expression involving subtraction like A − B is generally
treated as a shorthand notation for the addition A +
(−B). Thus, A − B contains two terms, namely A and −B.
This allows an easier use of associativity and
commutativity. |
|