|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
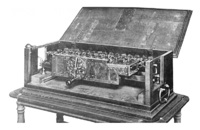 |
| Leibniz's Stepped
Reckoner was the first calculator that could
perform all four arithmetic operations. |
Arithmetic
Arithmetic (from the Greek ἀριθμός arithmos, 'number'
and τική [τέχνη], tiké [téchne], 'art' or 'craft') is a
branch of mathematics that consists of the study of
numbers, especially the properties of the traditional
operations on them—addition, subtraction,
multiplication, division, exponentiation and extraction
of roots. Arithmetic is an elementary part of number
theory, and number theory is considered to be one of the
top-level divisions of modern mathematics, along with
algebra, geometry, and analysis. The terms arithmetic
and higher arithmetic were used until the beginning of
the 20th century as synonyms for number theory, and are
sometimes still used to refer to a wider part of number
theory.
History
The prehistory of arithmetic is limited to a small
number of artifacts, which may indicate the conception
of addition and subtraction, the best-known being the
Ishango bone from central Africa, dating from somewhere
between 20,000 and 18,000 BC, although its
interpretation is disputed.
The earliest written records indicate the Egyptians and
Babylonians used all the elementary arithmetic
operations as early as 2000 BC. These artifacts do not
always reveal the specific process used for solving
problems, but the characteristics of the particular
numeral system strongly influence the complexity of the
methods. The hieroglyphic system for Egyptian numerals,
like the later Roman numerals, descended from tally
marks used for counting. In both cases, this origin
resulted in values that used a decimal base, but did not
include positional notation. Complex calculations with
Roman numerals required the assistance of a counting
board (or the Roman abacus) to obtain the results. |
|
 |
| Math signs. |
Arithmetic operations
The basic arithmetic operations are addition,
subtraction, multiplication, and division.
Addition
Addition, denoted by the symbol +, is the most basic
operation of arithmetic. In its simple form, addition
combines two numbers into a single number, the sum of
the numbers (such as 2 + 2 = 4 or 3 + 5 = 8).
Subtraction
Subtraction, denoted by the symbol -, is the inverse
operation to addition. Subtraction finds the difference
between two numbers.
(such as 4 - 2 = 2 or 8 - 5 = 3).
Multiplication
Multiplication, typically denoted by the symbol x.
Multiplication also combines two numbers into a single
number, the product.
(such as 2 x 3 = 6 or 3 x 4 = 12).
Division
Division, typically denoted by the symbol / is
essentially the inverse operation to multiplication.
Division finds the quotient of two numbers.
(such as 6 / 3 = 2 or 12 / 4 = 3). |
|
Arithmetic in education
Primary education in mathematics often places a strong
focus on algorithms for the arithmetic of natural
numbers, integers, fractions, and decimals (using the
decimal place-value system). This study is sometimes
known as algorism.
The difficulty and unmotivated appearance of these
algorithms has long led educators to question this
curriculum, advocating the early teaching of more
central and intuitive mathematical ideas. One notable
movement in this direction was the New Math of the 1960s
and 1970s, which attempted to teach arithmetic in the
spirit of axiomatic development from set theory, an echo
of the prevailing trend in higher mathematics.
Also, arithmetic was used by Islamic Scholars in order
to teach application of the rulings related to Zakat and
Irth. This was done in a book entitled The Best of
Arithmetic by Abd-al-Fattah-al-Dumyati.
The book begins with the foundations of mathematics and
proceeds to its application in the later chapters. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Search Fun Easy English |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
About
Contact
Copyright
Resources
Site Map |