|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
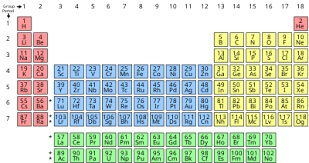 |
| The periodic table
of the chemical elements. |
Chemical Elements
A chemical element is a substance that contains only one
type of atom. If a substance contains more than one type
of atom, it is a compound. An element can be a solid,
liquid or gas. The smallest particle of such an element
is an atom. Atoms are made up of protons, neutrons, and
electrons.
Each element contains only one kind of atom. The number
of protons in an atom is called the atomic number. For
example, all atoms with 6 protons are of the chemical
element carbon, and all atoms with 92 protons are of the
element uranium.
The number of protons in the nucleus causes its electric
charge. This fixes the number of electrons in its normal
(unionized) state. The electrons in their atomic
orbitals determine the atom's various chemical
properties.
Elements are the basic building blocks for all types of
substances. When they are combined with each other, they
can form molecules.
118 different chemical elements are known to modern
chemistry. 92 of these elements can be found in nature,
and the others can only be made in laboratories. The
human body is made up of 26 elements. The last natural
element discovered was uranium, in 1789. The first
man-made element was Technetium, in 1937.
Chemical elements are commonly arranged in the periodic
table. Where the elements are on the table tells us
about their properties relative to the other elements. |
|
Chemical symbols
Chemical elements are also given a unique chemical
symbol. Chemical symbols are used all over the world.
This means that, no matter which language is spoken,
there is no confusion about what the symbol means.
Chemical symbols of elements come from their English or
Latin names. For example, carbon has the chemical symbol
'C', and sodium has chemical symbol 'Na', after the
Latin natrium. Tungsten is called 'W' after its German
name, wolfram. 'Au' is the symbol for gold and it comes
from the Latin word for gold, aurum. Another symbol
which comes from Latin is 'Ag'. This is the element
silver and it comes from the Latin argentum. Lead's
symbol, 'Pb', comes from the Latin plumbum and the
English word plumber derives from this as pipes used to
be made out of lead. Others were named after famous
people, like einsteinium, which was named after Albert
Einstein. |
|
Compounds
Elements can join (react) to form pure compounds (such
as water, salts, oxides, and organic compounds). In many
cases, these compounds have a fixed composition and
their own structure and properties. The properties of
the compound may be very different from the elements it
is made from. Sodium is a metal that burns when put into
water and chlorine is a poisonous gas. When they react
together they make sodium chloride (salt) which is
harmless and edible.
Mixtures
Some elements, particularly metal elements mix together
in any proportion to form new structures. Such new
structures are not compounds. They are called mixtures.
Isotopes
Most elements in nature consist of atoms with different
numbers of neutrons. An isotope is a form of an element
with a certain number of neutrons. For example, carbon
has two stable, naturally occurring isotopes: carbon-12
(6 neutrons) and carbon-13 (7 neutrons). Carbon-14 (8
neutrons) is a naturally occurring radioactive isotope
of carbon. Of each element, except for Ununoctium, at
least two isotopes are known. |
|
Classification
Elements can be classified based on physical states. At
room temperature and pressure, most elements are solids,
only 11 are gases and 2 are liquids.
Elements can also be classified into metals and
non-metals. There are many more metals than non-metals.
However, a few elements have properties in between those
of metals and non-metals. These elements are called
semimetals (or metalloids). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Search Fun Easy English |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
About
Contact
Copyright
Resources
Site Map |